
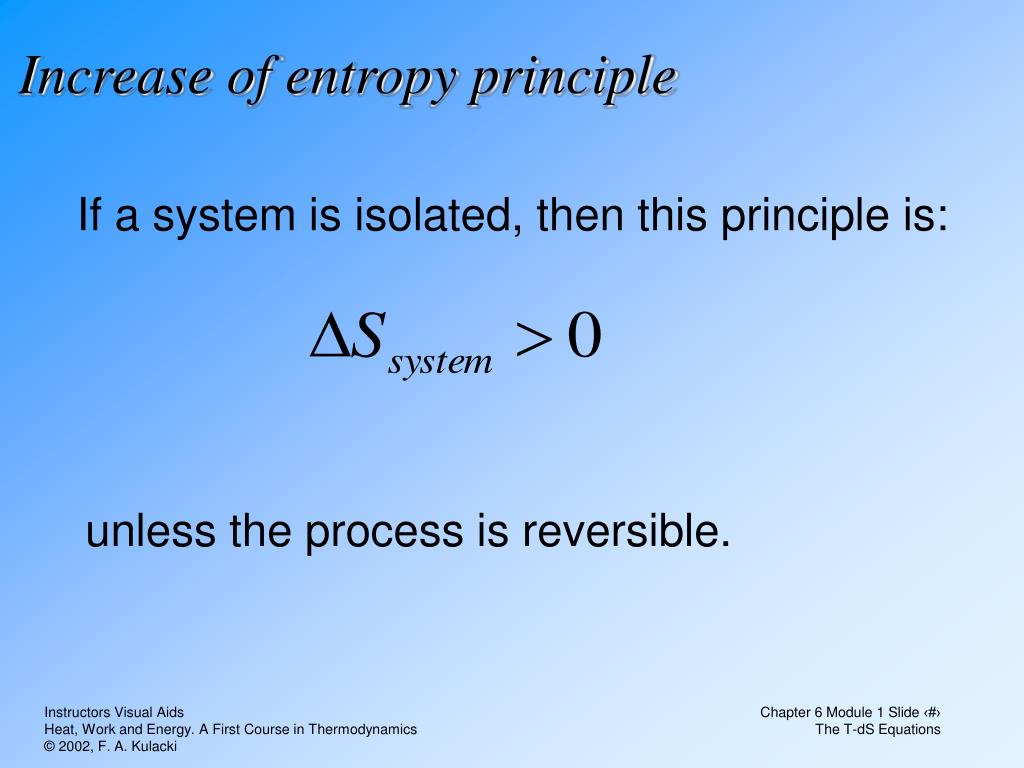
When a very large system exists in thermodynamic equilibrium, the quantity (Ω) denotes the total number of microstates accessible to the system, then:Įntropy is denoted by ‘S’ and its SI unit is Joules per kelvin (JK -1 ) or kg m 2 kg s -2 K -1 Enthalpy vs Entropy Source: CSBSJU The connection between thermodynamics and statistical mechanics is enshrined in the formula given by physicist Ludwig Boltzmann (1844-1906).
This entropy equation reveals that the amount of the material within a system and its current state affect the entropy value. In the case of a gas freely expanding in a vacuum, then the entropy change isĪnd when dQ’>dQ, the process is reversible. The value of work done is always less than the maximum possible work in any practical process because there are always some unavoidable energy losses due to friction and other reasons. Now, to balance the entropy change between system and the reservoir, the entropy change for system is increased as: If the change is internal energy (U) of the system during this process is dU, then:Īnd entropy change for the reservoir would be: So, when an opposing restraining pressure (P) is applied, the gas in the cylinder expands by dV volume in a reversible manner. To evaluate the entropy change for a system such as a gas cylinder equipped with a movable piston, let the gas intake dQ amount of heat at a given temperature (T). When entropy change is zero, a reversible process takes place, because in such a case even the smallest change is sufficient to run the heat engine backward. As per the second law of thermodynamics, the smallest possible value of entropy change (ΔS) is zero. Maximum work is done when the value of Q 2 is very small as compared to Q 1 but the value of Q 2 can not be zero because in such case, the entropy change turns out to be negative. Now, if there is a heat engine taking Q 1 amount of heat from one reservoir and Q 2 amount of heat from the other, then according to the law of conservation of energy, the work done (W) by the engine in one cycle would be:įor such system, the entropy change is calculated as If T 1 = T 2, then there is no flow of heat and the system is said to be in equilibrium In the case of two reservoirs with heat (Q) flowing through them and these reservoirs have temperatures ( T 1 and T 2 ). However, the entropy equation that is formulated for a heat engine is used more often because it efficiently describes both the second law of thermodynamics and the state of equilibrium for a system.Īccording to physicist Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888), if the temperature (T) for a heat reservoir is above zero and heat (Q) is flowing into the same reservoir then the entropy change or increase for such a system is given as: There are numerous equations that derive entropy in relation to different scientific parameters. Entropy Formulas and Equations Source: Kairen Bailey/Unsplash If energy input into the system, in the form of cleaning up and putting everything away, the room is returned to a state of order or low entropy. If no energy or work is put in, the room quickly becomes messy and disordered and has a high level of entropy. We can use the analogy of a teenagers' bedroom. High entropy means high disorder and low energy. The more energy that is lost by a system to its surroundings, the less ordered and more random the system becomes.

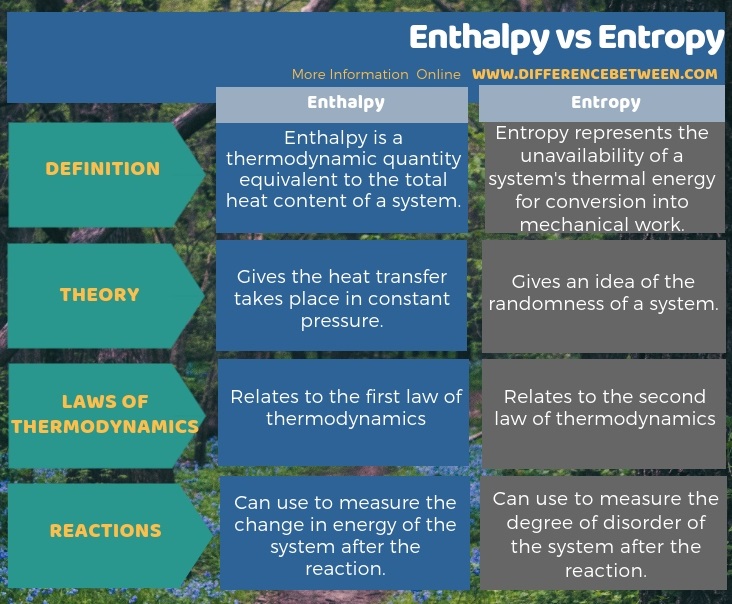
For example, if a system has a high value of entropy then it is difficult to predict the state of its atoms. However, a popular definition of entropy is that it is the measure of disorder, uncertainty, and randomness in a closed atomic or molecular system. It is also associated with the tendency toward disorder in a closed system.Įntropy is used for the quantitative analysis of the second law of thermodynamics. Different Definitions of Entropy Source: Research OutreachĮntropy is often referred to as the loss of energy available to do work. Moreover, entropy also tells us about the possibility of various chemical processes and the reason behind their reversible and irreversible nature. It serves as an integral principle of thermodynamics and it further led to the emergence of various mathematical principles and formulas related to probability. This peculiar phenomenon was elucidated in the 19th century from in-depth scientific research work on heat and energy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
